A Primer on Software-Defined WAN (SD-WAN)
Two decades ago, wide area networks (WANs) were designed to link local area networks (LANs) in order to connect physical geographical locations to one another, such as main headquarters and branch offices. Back then, data resided in physical locations like data centers and data movement was made possible through static, hardware-centric networks and expensive leased lines, dedicated fiber or virtual private networks.
Traditional WAN Challenges
As data continues to expand in size and variety, communication needs change and technologies evolve. Today, with the prevalence of the cloud and increased mobility, enterprises and workplaces are increasingly becoming virtual. Data now simultaneously resides in multiple locations, and the Internet has paved the way for a variety of transport protocols available for storing, accessing and retrieving data. In this ever-transforming and complex networked world, global enterprises need viable, less costly, more reliable and better-performing alternatives to traditional WANs.
Some of the most popular corporate WAN standards are multiprotocol label switching (MPLS), Frame Relay and Internet Protocol Security Virtual Private Networks (IPSec VPNs). MPLS is an IP-based protocol for transporting data within the same network. It is expensive, has low bandwidth, beset with performance and reliability challenges, and does not offer total control, as network configuration and traffic routing are done by the provider. Other WAN challenges include limited application awareness, fragmented security, complex operations and no readiness for cloud-based apps.
IDC Research conducted last year showed that the top challenges faced by today’s WAN are as follows:
- Security requirements relating to web, cloud services and Internet applications
- Complexity of multiple transport types, such as MPLS, Ethernet, Internet, leased lines, DSL, 4G/LTE
- Managing consistent user experience for on-premise enterprise apps and off-premises cloud applications (SaaS and IaaS)
- Simplifying WAN management and connectivity at remote branch offices
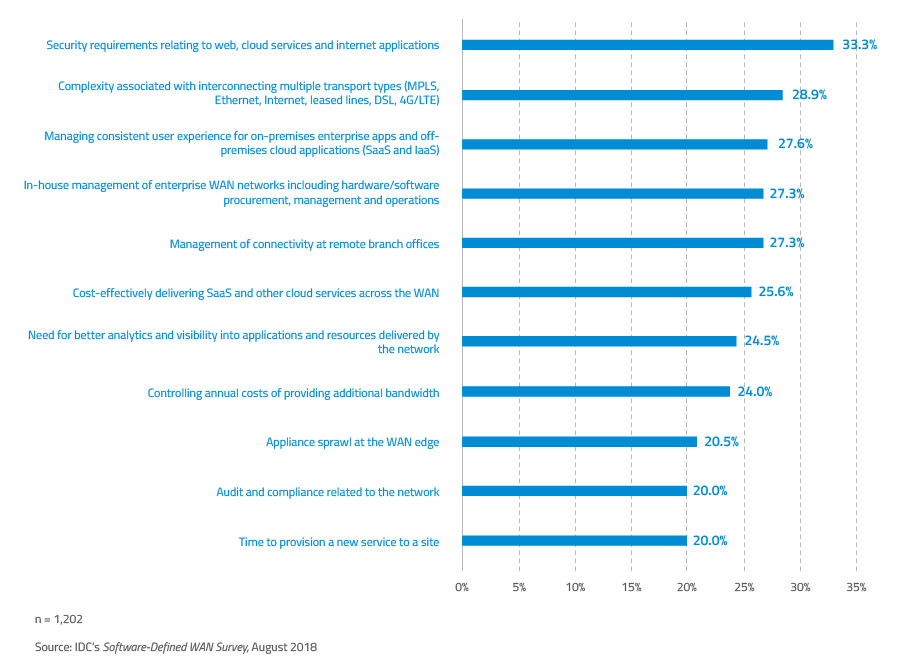
Figure 1. Top WAN challenges: Cloud security and rising WAN complexity
Today, a growing number of enterprises require flexibility to use a mix of traditional WAN technologies as well as new and emerging network technologies such as 3G/4G/LTE and broadband Internet as well as to reduce cost, provide better quality of service to apps, get better bandwidth and use cheaper commodity connections.
The Rise of Software-Defined WAN
Although experts point to the early 2000s as the period of SD-WAN’s inception, it was not until 2008 that the first reliable SD-WAN solution was made available to the market. As cloud security concerns and WAN management complexity increase, enterprises are considering SD-WAN as a viable option. SD-WAN offers a more flexible solution to hardware-centric WAN by optimizing multiple transport connections such as MPLS, broadband and LTE to intelligently steer traffic across the WAN.
According to the IDC study, SD-WAN adoption is gaining momentum, with 95% of enterprises surveyed already using SD-WAN solutions or intending to deploy SD-WAN solutions within a few months. The same research cites increasing cloud usage as the main driver of WAN technology choice, while the top drivers of SD-WAN adoption are secure cloud connectivity, performance of cloud apps and simplified WAN management.
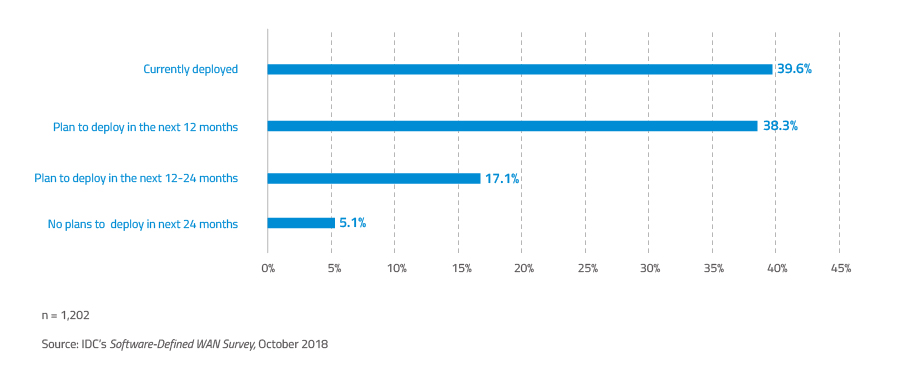
Figure 2. Nearly 40% of companies surveyed by IDC have already deployed SD-WAN solutions,
while over 55% plan to deploy SD-WAN in the coming months.
Why SD-WAN?
SD-WAN technologies transfer the burden of managing network traffic from hardware or physical devices to software. Here are some of SD-WAN’s key business benefits:
- Centralized control simplifies network management and improves the delivery of services, as it no longer requires managing individual gateways and routers. Complexity is greatly reduced with unified solutions that consolidate a wide range of services.
- Enhanced cloud application performance allows the classification and prioritization of the most important and most widely used applications. By being “application aware,” SD-WAN solutions can intelligently steer traffic according to user-defined application profiles and service-level agreements (SLAs).
- Zero-touch deployment delivers simplified deployment and security by allowing the automatic provisioning and configuration of SD-WAN appliances.
- Greater flexibility and agility with multi-connection and multi-transport options, allowing enterprises to select connection types and vendors most suitable for specific application needs.
- Higher return on investment (ROI) and lower total cost of investment (TCO) with increased bandwidth at lower costs.
SD-WAN结构概述
顾名思义,软件定义网络就是使用软件对WAN进行编程、配置和集中控制或管理,以智能地引导WAN上的流量。它利用多种传输协议来提供高速网络服务,以便企业可以快速访问应用程序和数据,并以较低的成本有效连接分支机构。
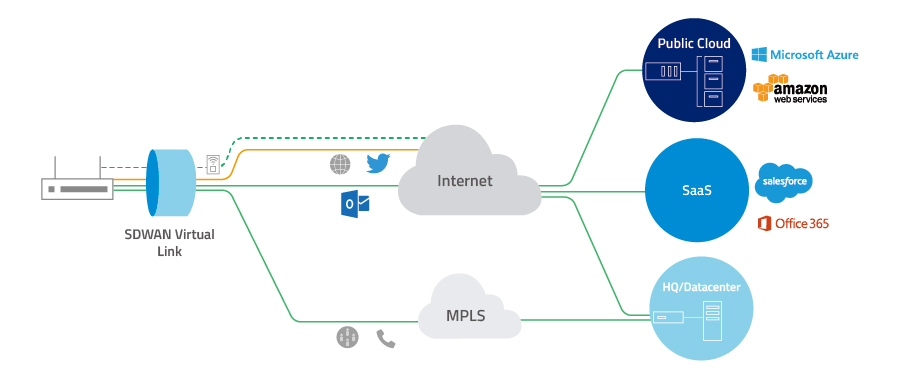
图3. SD-WAN使用多种传输协议来简化网络管理并改善网络服务(来源:Fortinet)
通过将硬件与集中控制和管理机制分离(虚拟化分离),SD-WAN可以提高业务灵敏性。
下图说明了这种分离的概念。
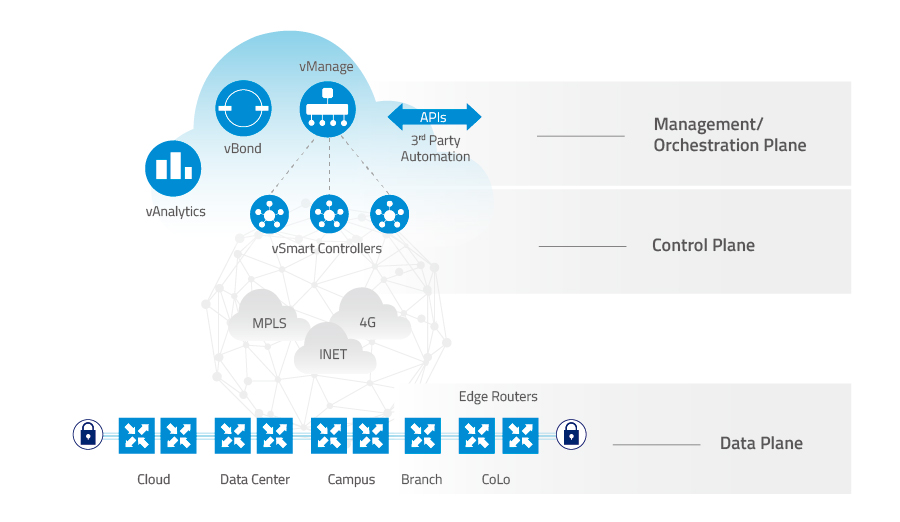
图4. SD-WAN结构以虚拟网络将数据平面与控制和管理机制分离。(来源:Cisco)
- 数据平面——也称为用户平面、转发平面、载体平面或承载平面。数据平面负责承载用户流量,支持与客户端之间的数据传输,通过多种协议处理多重对话并管理与远程节点的对话。 数据平面流量传输通过路由器而不是传入或传出于路由器。(来源:SearchNetworking)
- 控制平面——构建和维护网络拓扑,并决定流量的流向。控制平在网络中承载流量并负责路由选择。(来源:Cisco, SearchNetworking)
- 管理/编排平面。编排平面帮助将SD-WAN路由器自动加载到SD-WAN overlay虚拟网络层。管理平面负责中央配置和监视。.(来源:Cisco)
SD-WAN组件
城域以太网论坛Metro Ethernet Forum (MEF)是一个非营利性国际行业联盟,拥有200多家成员公司,它正在努力为“覆盖全球自动化网络生态系统的敏捷、有保证和精心安排的服务”制定发布行业技术标准。它概括了提供SD-WAN服务所需的组件:
- SD-WAN Edge。这可以是物理设备,也可以是基于虚拟网络功能(VNF)的虚拟客户驻地设备(CPE)。它位于网络的边缘(边界),允许内部网络连接到外部网络。它还执行其他重要功能,例如基于应用程序的服务质量(QoS)、执行安全策略和优化WAN功能。
- SD-WAN网关允许通过SD-WAN连接的站点连接到使用其他VPN技术互连的站点。
- SD-WAN控制器集中管理所有SD-WAN Edge和SD-WAN网关的物理或虚拟设备。
- 服务编排器提供SD-WAN服务生命周期的管理,包括服务实现、性能、控制、保证、使用、分析、安全和策略。
- 用户网络门户通常集成到其他管理服务的现有客户门户中。激活这些服务后,用户网络门户与服务编排器进行通信以进行SD-WAN服务修改,例如根据用户角色设置不同的QoS、安全性或业务策略。
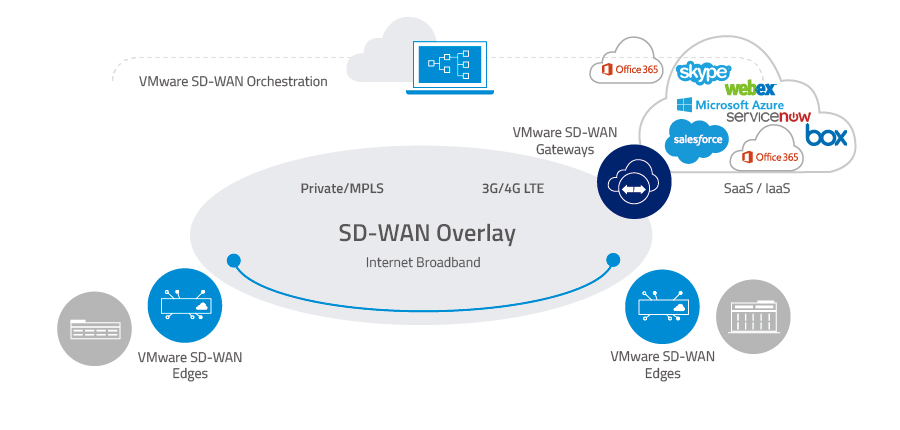
图5. SD-WAN 组件
来源:Velocloud
ATP与SD-WAN
ATP Electronics是工业专用DRAM模块和NAND闪存解决方案的领先提供商,已为满足SD-WAN Edge器件和设备的内存和存储需求做好准备。ATP的产品经过精心设计、专业制造和严格测试,即使在最恶劣的工作环境中也能提供最高水平的性能、可靠性和耐用性。
ATP的Edge解决方案
ATP的内存和存储解决方案是专为企业设计和制造的,便于企业轻松、简单地实施SD-WAN,同时确保最高的可靠性、巨大的价值和最佳的总体拥有成本(TCO)。
- 专为超紧凑型设备而设计。ATP产品尺寸小巧,以适应现如今设备开发中对压缩空间的需求,同时在可靠性、耐用性和数据安全访问等方面具有重大优势。
- 先进的电源管理和低功耗。ATP解决方案使用最新的电源管理技术,可优化功耗以节省大量电能。对于某些产品,板载了先进的断电保护机制,可在断电时保护数据和设备。
- 严谨的测试和验证。作为一家真正的制造商,ATP管理制造过程的各个阶段,并从晶圆/IC级别到模块和产品级别进行全面测试,以确保从其工厂出产的产品都是质量最高的。
- 受控BOM。通过保持对供应链的完全控制,ATP实施受控物料清单(BOM),以确保较长的产品周期和缓冲库存与销售预测相一致,并与客户密切配合,满足长期的供应需求。
- 最佳的总体拥有成本值。可靠的性能和延长的使用寿命可最大限度地减少宕机时间,延长使用寿命,减少更换次数。总体而言,这些优势可带来高投资回报(ROI)和最佳总体拥有成本。
ATP的SD-WAN内存和存储解决方案针对边缘设备、主机或预置云网关、编排器以及其他分支机构或数据中心设备进行了优化。它们有各种外形尺寸、容量、工作温度和定制功能可供选用。
|
ATP内存解决方案 |
|
|
Generation |
DDR4 / DDR3 |
|
Form Factor |
Non-ECC/ECC SO-DIMM |
|
Density |
4 GB / 8 GB / 16 GB / 32 GB |
|
Speed (MT/s) |
3200 / 2933 / 2666 / 2400 / 2133 /1866 / 1600 / 1333 / 1066 |
|
ATP NAND闪存解决方案 |
||||
|
|
Form Factor |
Capacity |
Possible ATP |
可选性能 |
|
SSDs |
M.2 2242 SATA |
16 GB / 32 GB / 120 GB / 240 GB |
16 GB to 32 GB: A600Sc (MLC C-Temp) |
|
|
120 GB to 240 GB: A600Vc (3D TLC C-Temp) |
||||
|
mSATA |
16 GB |
A600Sc (MLC C-Temp) |
||
|
Managed NAND |
e.MMC |
16 GB |
16GB: E600Si (3D NAND MLC) |
|
表1.用于SD-WAN的ATP工业专用存储器和NAND闪存解决方案
想要了解更多,请访问ATP网站或联系ATP代表/经销商。