During a sudden power loss event, the host system is unable to perform a normal power shutdown that allows data to be safely transmitted or “flushed” from the cache to the NAND flash memory. To protect in-flight data, the host promptly issues a flush cache command to the solid state drive (SSD).
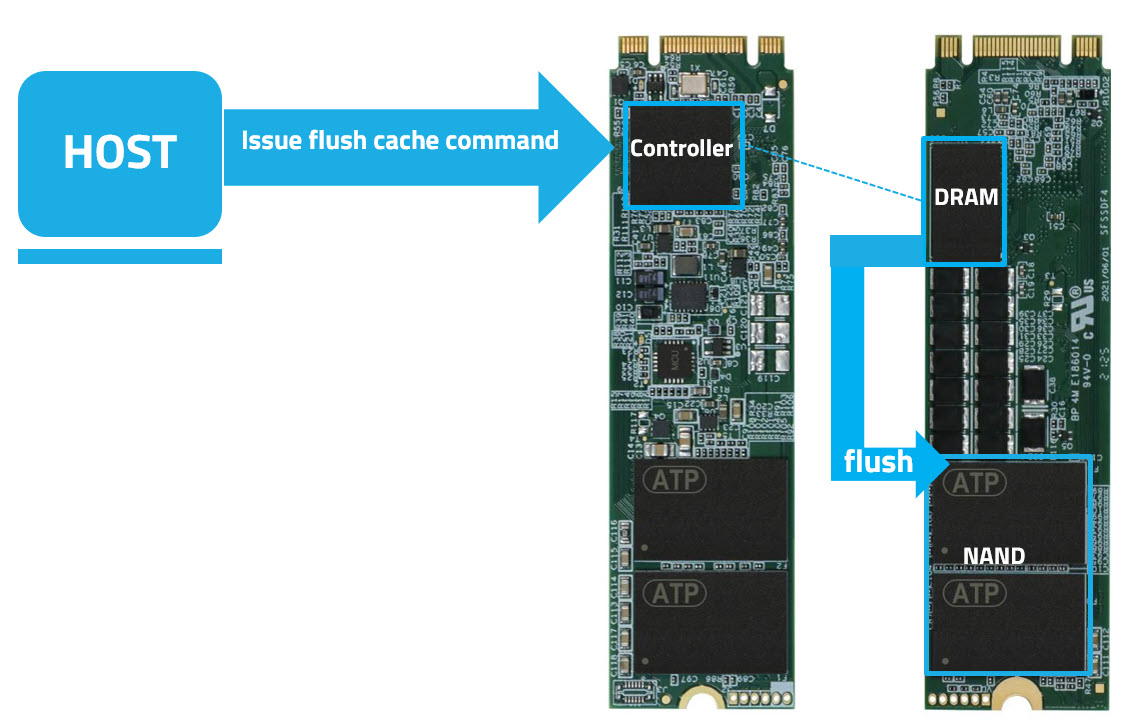
Some networking/server appliances, however, in order to avoid in-flight data staying in the cache, issue excessive and unnecessary flush commands to the SSD in an effort to prevent or minimize data loss.
The Challenge
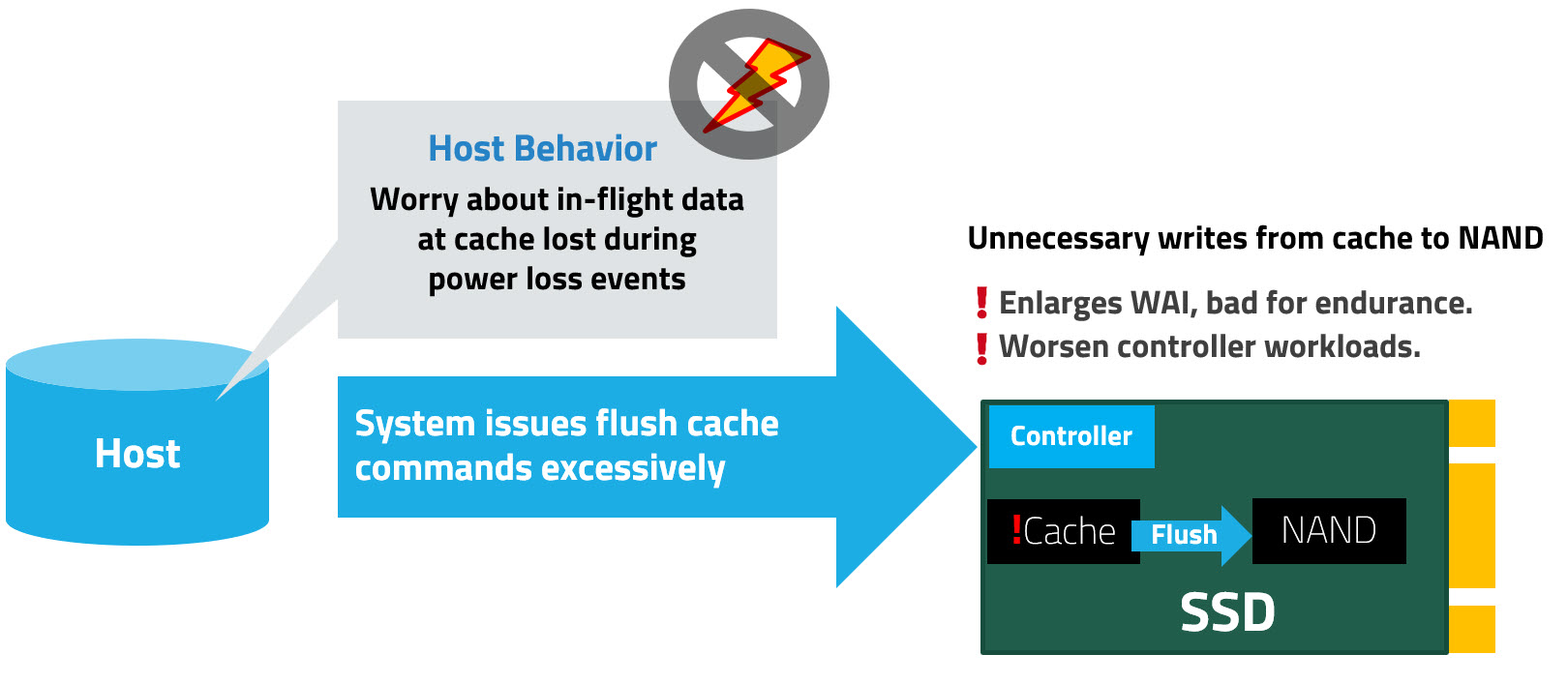
Flush commands frequently issued by certain host systems come at the cost of excessive writes that do not only accelerate NAND flash wear but also exact a toll on controller workloads that cause performance slowdown and drastically increase the Write Amplification Index (WAI), as the SSD is writing more data than necessary, thus jeopardizing NAND endurance.
The Problem with Excessive Flush Commands
Flush commands are necessary to ensure that data temporarily stored in the cache is safely moved to the non-volatile NAND flash memory; however, when these commands are issued by the host too frequently, they result in:
- Higher WAI and Accelerated Wear. WAI refers to the ratio of writes committed to the flash memory to the writes from the host system. As each flush involves multiple writes, the amount of data written to the flash exceeds the amount of data that the host requires to be written, thus unnecessarily amplifying the write cycles. A high WAI degrades the SSD and reduces the SSD’s lifespan.
- Performance Degradation. The frequent flushes disrupt the SSD’s ability to handle other important operations, thereby adversely impacting random write performance.
The ATP Solution: EcoFlush Technology for Intelligent Flush Management
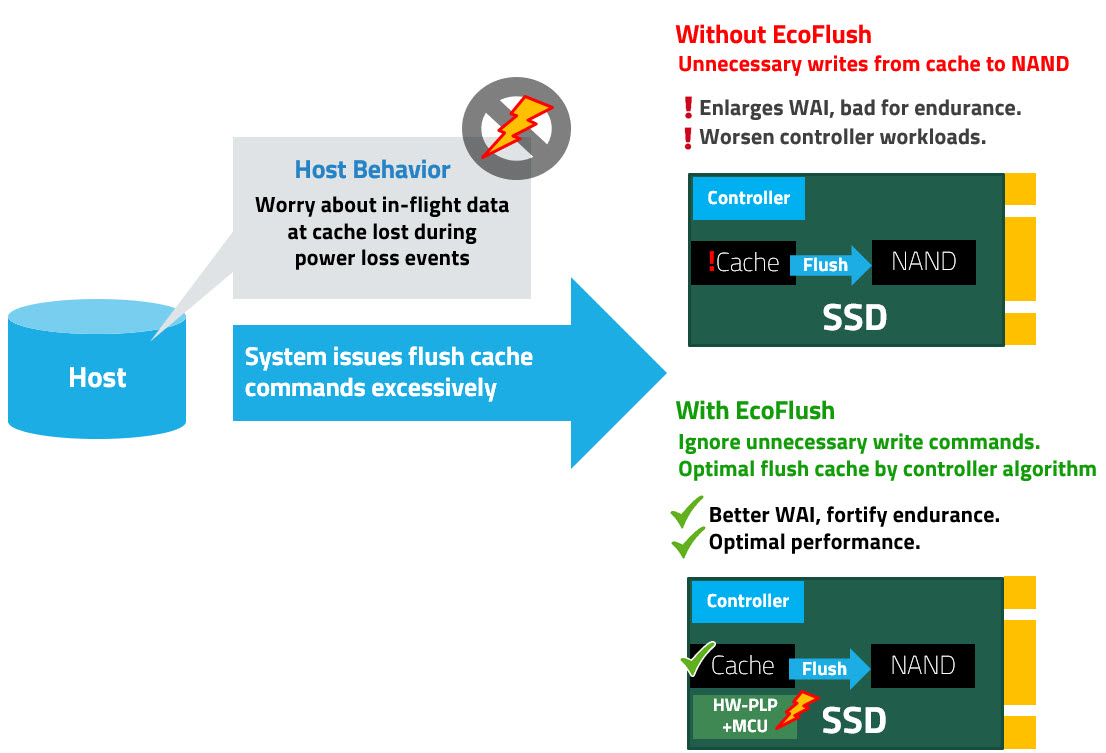
ATP Electronics’ hardware power loss protection (HW PLP) design is already robust and provides excellent in-flight data protection during sudden power loss events. To address the aforementioned challenge, ATP raises the bar with its proprietary EcoFlush firmware combined with its top-notch HW PLP. EcoFlush is an optional feature, which may be enabled by request. Once enabled, EcoFlush intelligently bypasses the host’s excessive flush commands and instead runs the flush cache based on ATP’s own FW algorithm.
EcoFlush Mechanism: How does it work?
The ATP HW PLP mechanism protects the in-flight data, while EcoFlush optimizes performance and endurance.
EcoFlush bypasses the flush cache command from the host when:
- HW PLP protects the in-flight data
- EcoFlush is enabled by ATP at SSD initialization (optional, enabled by request)
- The SSD still runs flush cache behavior at optimal intervals
Benefits
EcoFlush offers the following benefits:
- Optimized Flush Intervals. Instead of responding to all the host’s flush commands, EcoFlush intuitively determines flush optimal intervals depending on the SSD’s workload.
- Customizable, Seamless Hardware Integration. EcoFlush is integrated into SSDs with HW PLP, and may be activated, upon customer request, during SSD initialization at production stage without requiring modifications on the host system.
- Lower TCO. Longer endurance and better performance minimize drive replacements and maintenance, maximize usability, all translating to lower total cost of ownership and higher cost efficiency.
- Extended Drive Endurance and Improved Performance. By reducing the unnecessary writes from frequent flushes, EcoFlush accomplishes the following, under certain conditions:
- 10X Lower WAI. This translates to lower write cycles, ultimately prolonging the SSD’s operational lifespan.
- 11X higher 4K Random Write Performance. Freed from distracting operations, the SSD random write performance is significantly improved to support demanding workloads without compromising data integrity.
The following graph is from a real case result, based on specific test patterns, showcasing how EcoFlush improves sequential and 4KB random write performances, as well as lowers WAI value compared with SSDs that do not have this feature.
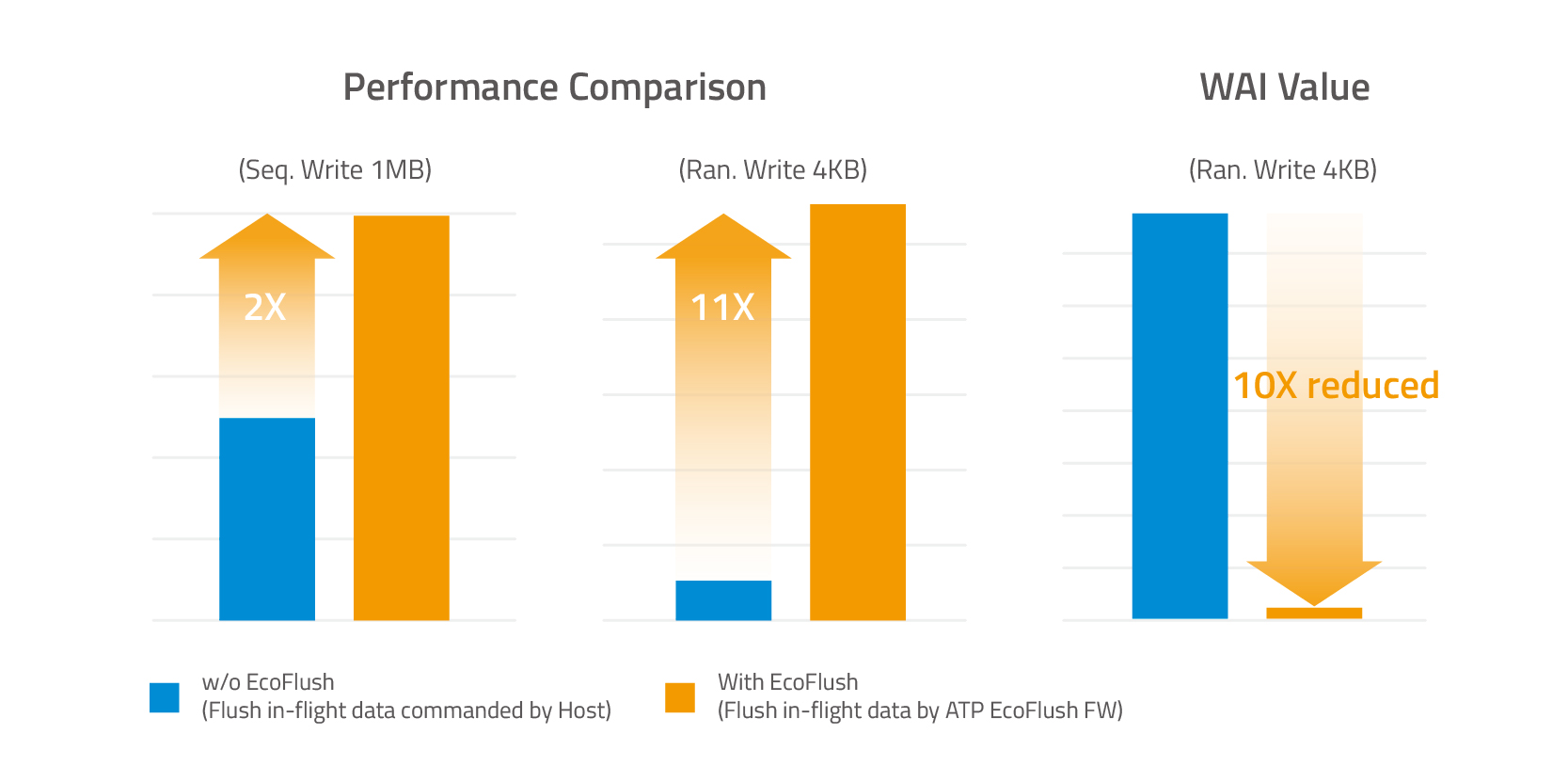
EcoFlush delivers 2X improvements on Sequential Write Performance, 11X better Random Write Performance, and 10X lower WAI compared with SSDs that only flush in-flight data as commanded by the host.
Use Case Scenario: Abnormal Performance Drop on Servers
Problem
A cloud service provider noticed an abnormal performance drop in their SSDs. After investigation, the root cause was identified as the host too frequently commanding the SSDs to flush their cache. This mechanism has been embedded in the software stack for generations, so the service provider prefers not to rewrite its flush command behavior.
ATP Solution
Frequent flush commands are unnecessary and can actually create more problems. To address this, ATP offers the “EcoFlush” feature on its SSDs to complement the microcontroller unit (MCU)-based HW PLP. EcoFlush is optional and may be activated at initialization stage upon the customer’s request.
When enabled, EcoFlush ignores unnecessary flush commands from the host. This allows the system to enjoy maximum SSD performance. Additionally, the wear on NAND is greatly reduced, further eliminating endurance concerns over time.
The following illustrates how excessive flush commands from the host can jeopardize SSD endurance and worsen controller workloads. In contrast, by ignoring unnecessary write commands, EcoFlush optimizes flush cache, which results in better WAI, fortified endurance, and optimal performance.
Conclusion
ATP persistently and consistently delivers innovative solutions like EcoFlush Technology to further advance its already-robust hardware power loss protection mechanism. With EcoFlush activated and bypassing the host’s excessive flush cache commands, ATP SSDs deliver data integrity and drive longevity, making them ideal for demanding applications that require utmost reliability and endurance.
For more information on the ATP EcoFlush Technology, visit the ATP website or contact an ATP Representative in your area.


