ATP solid state drives (SSDs) often operate in a variety of applications under extreme conditions. They may be installed in systems where the temperature can alternate between extremely hot and extremely cold. In some instances, power supply may be unstable and sudden power-off events may occur. Under such circumstances, these SSDs should continue to perform with high reliability and be able to endure such conditions while maintaining device and data integrity.
To determine the SSD’s resistance to these harsh conditions, ATP performs the following tests on SSDs with power loss protection (PLP) mechanism to demonstrate that even at extreme temperatures and voltages at sudden power off and unstable power supply, the SSDs can still perform reliably and are able to handle stored data without data miscompare.
Operating Temperature Cycling Test. This determines the SSD’s ability to resist extremely high and extremely low temperatures, which can wreak havoc on the integrated circuits, the NAND flash, solder joints and other critical parts of the SSD. ATP’s operating temperature cycling test incorporates power cycling and burn-in (BI) testing with four-corner matrix of high/low voltage vs. high/low temperature. This simulates the drive’s reliability under extreme system instability and diverse operating conditions.
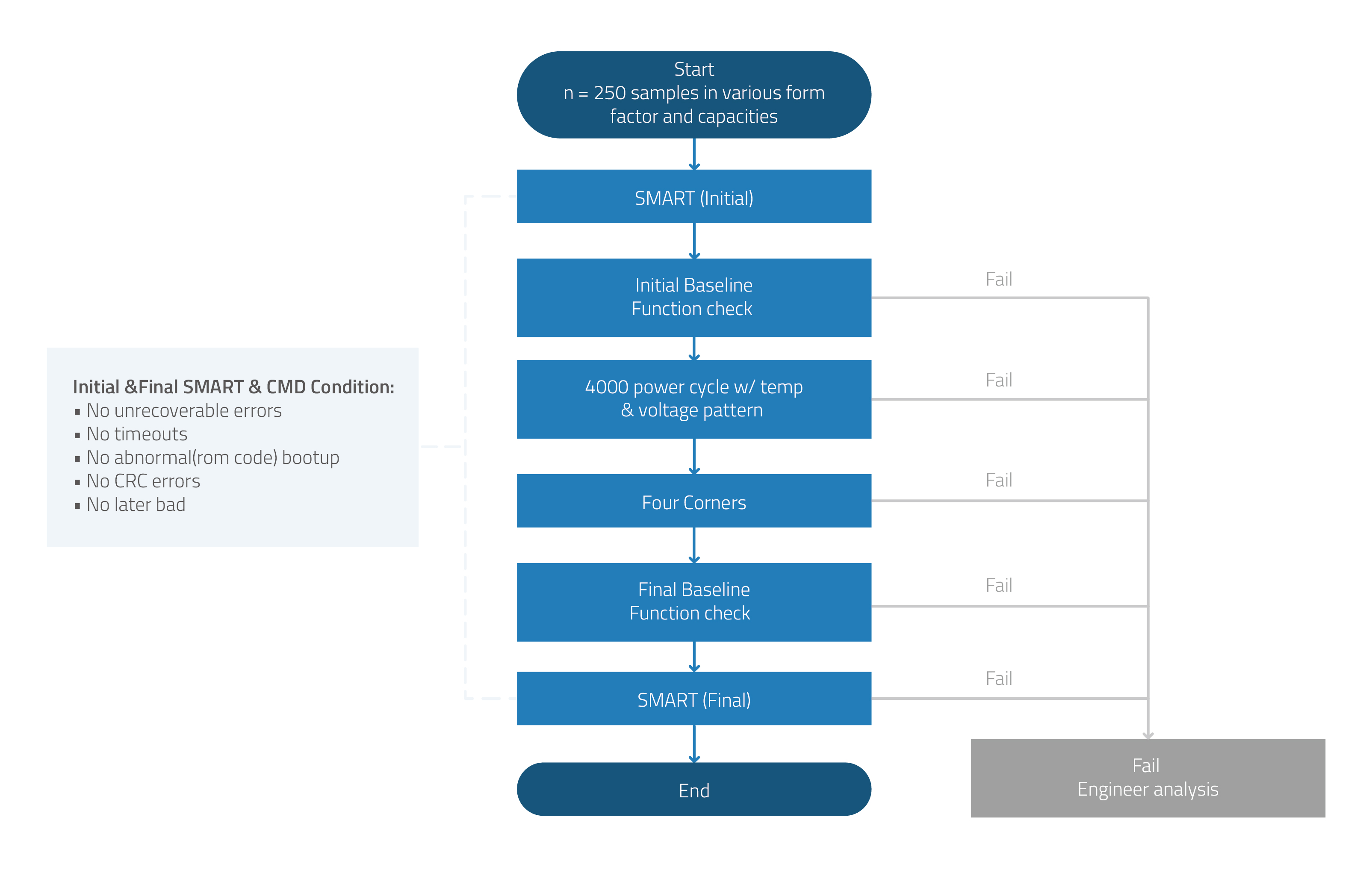 Figure 1. Operating Temperature Cycling Test Flow
Figure 1. Operating Temperature Cycling Test Flow
Sudden Power-Off Cycling Test. This test validates the design of the PLP mechanism under sudden power-off conditions. A data pattern is written onto the SSD, and power is then cut off while data is being programmed into the NAND flash blocks. By creating a sudden power failure at the “write” command stage, the test proves the effectivity of the PLP mechanism, showing a “Pass” after 4000 power cycles without any data errors.
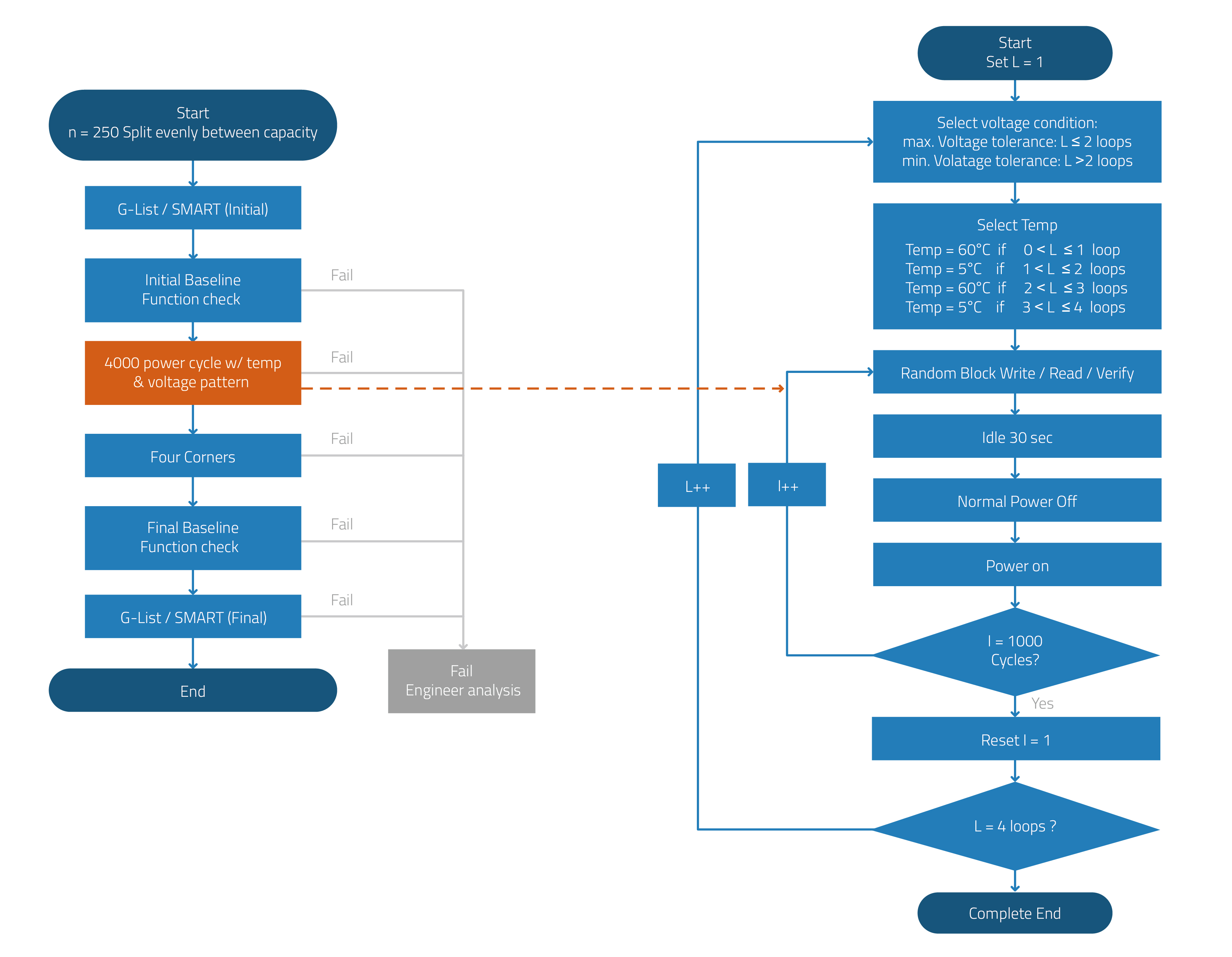 Figure 2. Sudden Power-Off Cycling Test Flow
Figure 2. Sudden Power-Off Cycling Test Flow
The following figure shows a sample graph of a Power Cycling test, where the SSDs are subjected to numerous cycles of the following conditions:
- High temperature – High voltage
- Low temperature – High voltage
- High temperature – Low voltage
- Low temperature – Low voltage
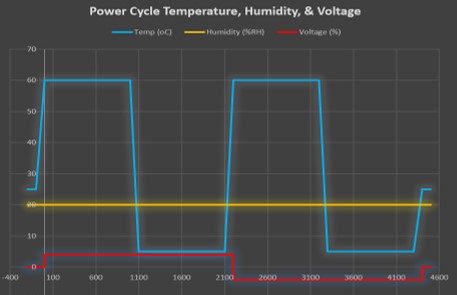
Figure 3. Sample graph of temperature, humidity, and voltage in a Power Cycling test
The above graph shows the Power Cycling test aiming to simulate diverse operating conditions, such as extreme temperature and voltage changes that may affect the performance and life span of the drives. After subjecting its SSDs to 4000 power cycles with the above testing conditions, ATP’s PLP mechanism can effectively handle sudden power losses and voltage fluctuations without data errors.
Four-Corner Testing. Operating temperature and input voltage can impact SSD functionality. Each of these can individually impact SSD performance and life span but combining various parameters at extreme levels can bring out product weaknesses and issues faster. Four-corner testing refers to functionality tests performed at four quadrants or combinations of test conditions: the maximum/minimum values of operating temperature and input voltage. The SSD goes through several cycles of repeated data reading and data writing to verify its performance at different levels of each condition in the quadrant.
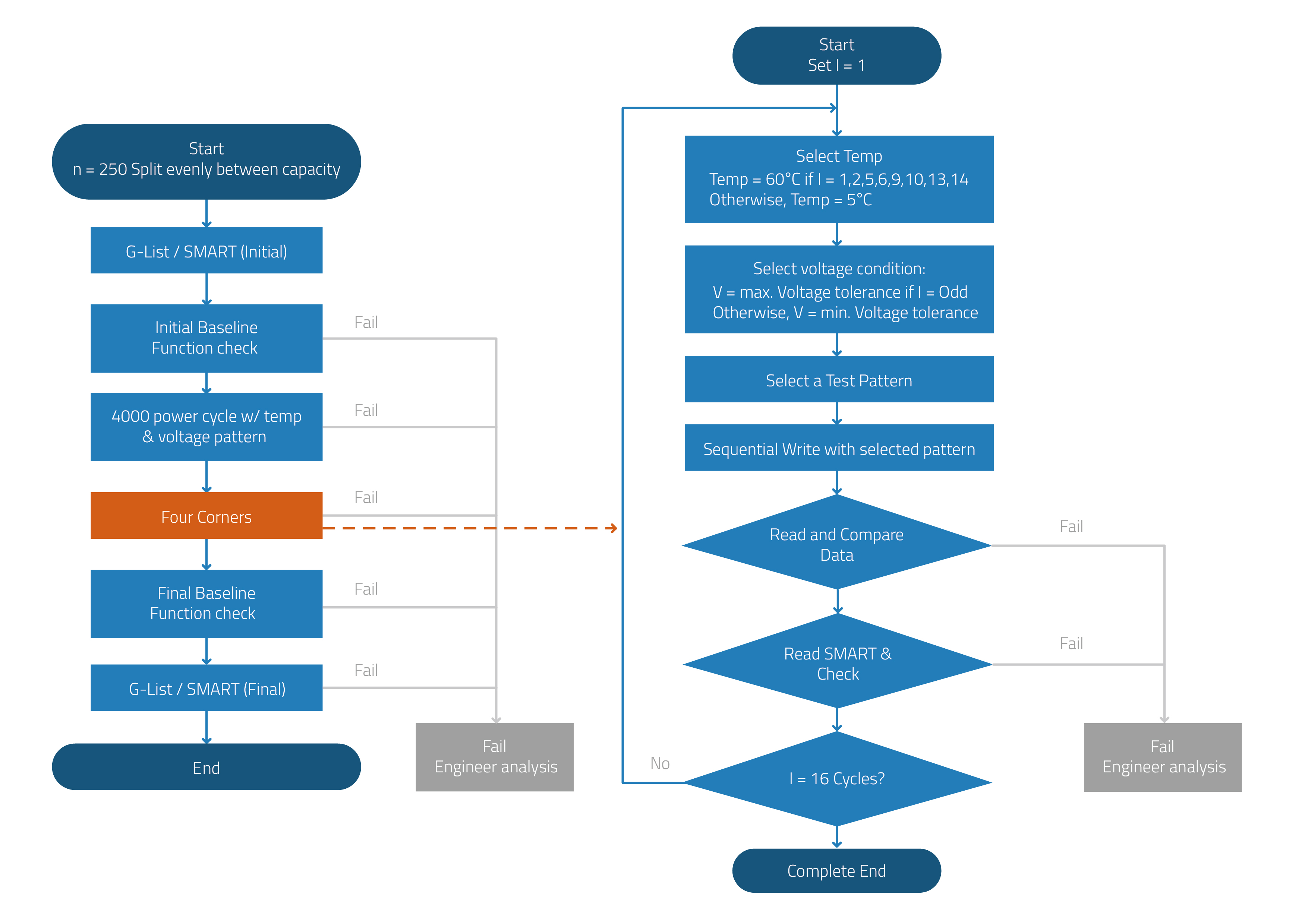
Figure 4. Four-Corner Test Flow
The following figure shows sample graphs of Four-Corner testing, where the SSDs are subjected to numerous cycles of the following conditions, with each condition lasting several hours:
- High temperature – High voltage
- High temperature – Low voltage
- Low temperature – High voltage
- Low temperature – Low voltage
…
…
- High temperature – Low voltage
- High temperature – High voltage
- Low temperature – Low voltage
- Low temperature – High voltage
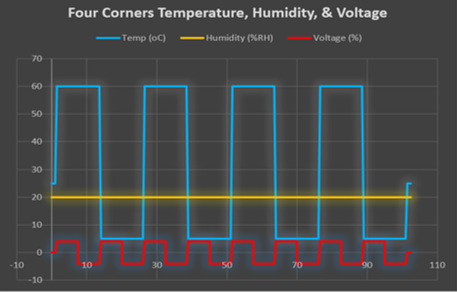
Figure 5. Sample graph of temperature, humidity, and voltage in a Four-Corner test
The above graph shows the rigorous testing that ATP SSDs go through to demonstrate their reliability in harsh operating conditions, making them suitable for mission-critical applications that require consistent performance and long endurance. Even at different levels of temperature and voltage, ATP SSDs meet and even exceed operating tolerances.
Key Takeaways
Sudden power loss events and extreme operating temperatures pose constant challenges to device and data integrity. ATP’s Four-Corner, Temperature Cycling, and Power Cycling tests provide assurance that SSDs continue to perform reliably and maintain data integrity even when operating under harsh and unstable conditions. ATP SSDs go through numerous cycles of these tests for several hours without data miscompare, demonstrating high reliability and quality that make them suitable for applications that require dependable performance in the toughest conditions.
ATP’s Four-Corner, Temperature Cycling, and Power Cycling tests are part of the many reliability and endurance tests developed and performed by ATP to ensure strict compliance to the highest standards of quality. ATP is committed to deliver high-performance and high-endurance NAND flash storage products to ensure the best value for total cost of ownership (TCO).
For more information on ATP’s testing processes and for customization requests, visit the ATP website or contact an ATP Representative.