3D Memory Cards for IoT/IIoT Gateways
A gateway is an important component of the Internet of Things (IoT) and industrial IoT (IIoT) ecosystem. As its name implies, a gateway is a device that connects things (sensors, actuators, and intelligent devices) to the cloud, functioning as a bridge or intermediary where all data going to or coming from the cloud goes through. For data that may not have to be transferred to the cloud, a gateway also provides storage and fast analytics at or near the source to enable intelligent, time-critical decisions.
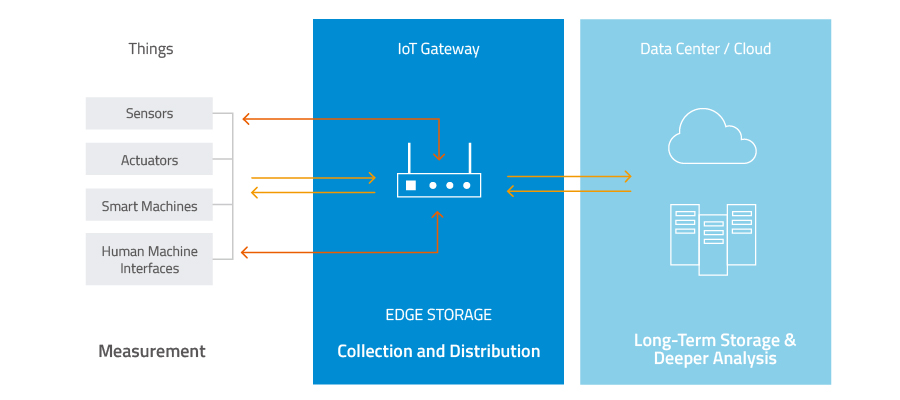
Figure 1. An IoT gateway acts as a bridge between IoT/IIoT devices and the cloud, serving as temporary repository or as storage device for data that may not need to go to the cloud.
Cloud vs. Edge Storage
Data is transforming the way industries operate. In the field of energy exploration alone, a typical offshore oil platform in a remote location generates 1 TB to 2 TB of data daily. Most of the data, which come from sensors, surveillance cameras and many other sources, are time sensitive. Moving all this data to a central location using satellite connection, however, could take about 12 days.
Cloud storage refers to storing and accessing data over the Internet. It allows retrieval of files from any device in any location as long as Internet connection is available. Several users may access the same files simultaneously if they have the necessary passkey. Due to limited bandwidths, costly network services, and unstable connection in some areas, relying on the Internet may result in delays that will render the data irrelevant or cause risks to life or property especially for applications that require real-time processing and retrieval.
Edge storage refers to storing, analyzing and processing critical data at or closer to the data source rather than in a centralized or cloud-based location. It offloads the network, cuts transmission costs, and optimizes the data collected for immediate insight or swift response. In applications where data needs real-time processing and does not have to be stored in a central location for data warehousing or deeper analytics, edge computing is a more viable alternative.
|
Cloud Storage |
Edge Storage |
|
|
Table 1: Ideal use cases for cloud and edge storage
The Importance of Gateways in the IoT/IIoT Ecosystem
Whether data will ultimately be transferred to the cloud or will stay on the premises, gateways are important components of the IoT/IIoT ecosystem. Why do we need gateways? Why not send all data gathered by sensors and devices directly to the cloud? In the IoT/IIoT, every connected device generates astronomical amounts of data. Sensors alone easily create a deluge of data by the second; however, they have limited networking connectivity capabilities. With gateways, sensors can have a single point of contact to external networks.
Below are some of the advantages of using IoT/IIoT gateways:
-
Data Filtering, Aggregation and Volume Minimization. By pre-processing data at the edge, IoT/IIoT gateways provide critical analysis closer to the source, so not all data have to be transmitted to the cloud. This prevents the sheer volume of unnecessary data from inundating the network and resulting in higher transmission and storage costs.
Pre-processing before data is sent to the cloud can include converting the data to another format, packaging, validating, and sorting according to a particular sequence. It could also mean eliminating unnecessary details or aggregating/summarizing data for analysis. When data is pre-processed on-site or close to the source, information can be transmitted to the cloud in smaller footprints. -
Faster Response Times and On-Site Intelligence. By providing local processing and storage capabilities, IoT/IIoT gateways enable near-real-time delivery of services, insight and control over connected devices.
-
Reliable Offline Operation. Internet connectivity has advanced by leaps and bounds, but occasional outages, slow connections, low bandwidth and other issues still hover. In some cases, failure of Internet connections can cause undue risks to assets and infrastructure, and negatively impact business decision making. Gateways provide Internet-independent dependability, allowing reliable backup to ensure uninterrupted communication and control.
-
Better Security. Since sensors and devices are connected to the gateway and not directly to the Internet, this reduces the vulnerability of sensors/devices getting hacked. Gateways protect the data being transmitted to the cloud from leaks, and prevent unauthorized control of sensors and devices.
Common Storage Challenges for Gateways
In this age when data is touted as the new currency, the IoT/IIoT presents numerous opportunities for transforming businesses using actionable insights. Fast, secure intelligence at the edge enables real-time analysis, which in turn translates to better processes and better bottom lines.
As billions of connected devices whip up immense amounts of data by the second, what are some of the most common requirements for storage in this increasingly expanding IoT network?
-
Space Constraints. Most IoT/IIoT devices and components such as gateways are small, as they are typically deployed in settings with space limitations. Memory solutions must therefore be compact, without compromising performance and storage capabilities.
-
Diverse Usage. Data from sensors and devices typically vary from large files such as those generated by surveillance cameras and tiny log files from environmental sensors. The wide gamut of application usages reflects vastly different input/output profiles, such that it is nearly impossible for a one-size-fits-all solution.
-
Demanding Environments. It is not uncommon for gateways to operate 24/7, as sensors and devices are always on "live" mode and endlessly churning out streams of data. Dust, shock and vibration, and electrostatic discharge (ESD) on site require storage solutions that are robust and able to withstand such conditions. Ultra-compact gateways are usually fanless and storage solutions should also be able to endure wide temperature variations while stored and in operation.
-
Data Reliability & Integrity. Devices deployed for industrial applications commonly face power losses and voltage fluctuations that could lead to data loss. As gateways typically hold both static and dynamic data in mixed workload scenarios, it is important to make sure that such data is protected from power loss and data corruption.
ATP 3D NAND-Based Memory Cards Meet Growing IoT /IIoT Storage Needs
ATP's industrial-grade SD and microSD cards based on 3D NAND technology meet the growing data storage needs of the IoT/IIoT. Thanks to these tiny and low-power yet powerful removable data collection solutions, gateways can store huge amounts of data closer to the source, providing local intelligence and ensuring Internet-independent operation even in the event of connection outages. Memory cards are also used as handy boot devices, conveniently storing the gateway operating system.

Figure 2. ATP SD and microSD memory cards based on 3D NAND technology
-
Small Cards, Big Performance. ATP memory cards based on 3D NAND technology provide compact, robust and reliable storage whether locally or at the edge. Engineered to meet the escalating storage demands of the IoT/IIoT, ATP 3D memory cards offer high capacities for data-rich applications. Additionally, A1 performance rating ensures fast random read-write and sustained sequential read-write performance. High-density and high-performance storage made possible through 3D NAND technology enables swift processing to deliver time-critical analytics near real time. The compact form factor offers small footprint ideal for space-constrained systems without compromising performance.
- Convenient Portability. Removable storage devices like ATP's memory cards make it convenient to swap application programs and transfer files. It is also easy to replace memory cards; and, thanks to their compact size, they are light enough to bring to other locations.
- Wide Temperature Support. ATP 3D memory cards are built based on floating gate architecture, which is a proven technology found most suitable for wide temperatures. With industrial temperature ratings of -40°C to 85°C, these memory cards can be depended on even in extreme temperatures.
- Rugged Design. System-in-Package (SiP) technology fortifies the durability of ATP 3D memory cards by encapsulating all exposed components, thus making the cards resistant to damaging elements such as dust, humidity, ESD, shock/vibration, and more.
- Built to Endure. NAND flash products built on the new process technology offer larger capacities but can potentially have higher bit error rates and lower endurance. ATP 3D memory cards are built with multi-level cell (MLC) flash, taking advantage of all the benefits of 3D NAND technology without compromising endurance and data retention. The single-level cell (SLC) mode of ATP 3D memory cards can be an option for write-intensive environments, having 8-10 times higher endurance at half the density of other solutions.
- Maximum Dependability. ATP 3D memory cards provide peace of mind, providing reliable backup and ensuring that data on-demand is available even when Internet connection is not available. In the event of power supply loss or fluctuation, Sudden Power-Off Recovery (SPOR), a firmware-based backup mechanism, ensures data integrity by effectively tracing and recovering previous valid data when power comes back on. In addition, the data refresh algorithm keeps the integrity of data by preventing read disturb errors and a life monitor tool provides an easy way to check the health status of the memory cards.
- Better Privacy Control. Gateways provide local analysis of sensitive data for better privacy control, enabling data and generated insights to be more closely monitored and controlled. ATP memory cards fortify protection by building a security key that allows the gateway to recognize only qualified memory cards with the correct key, thus preventing unauthorized cards to be used on the gateway.
ATP 3D memory cards are ideal for industrial applications requiring secure, on-demand storage and backup such as building automation, maintenance and asset management, health care, security and surveillance systems and manufacturing, as well as automotive and transport applications such as advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), in-vehicle infotainment (IVI), telematics, navigation and fleet management. As storage devices for IoT/IIoT gateways and other edge devices, ATP 3D memory cards allow critical data to be stored and processed close to the source to provide local intelligence and insights that could transform businesses.
For more information on ATP memory cards, please visit the ATP website or contact an ATP Distributor/Representative in your area.