What is NVMe?
NVM Express®, also known as NVMe™, is an interface specification optimized for NAND flash and next-generation solid state storage technologies. This interface is defined to efficiently support the needs of enterprise and client systems utilizing PCI Express® (PCIe®) solid state drives.

Why do we need another interface specification?
Over the years, CPU and DRAM speeds have increased, but mechanical drives and interfaces used to connect them have not kept up. The NVM Express Work Group, made up of leading technology manufacturers, developed NVMe to narrow the growing gap between fast DRAM and slow storage.
What is PCIe and why is NVMe optimized for PCIe-based SSDs?
PCIe, which stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect Express and also known as PCI Express, is an I/O interconnect interface that was designed as a high-speed replacement for aging standards like PCI and AGP. PCIe typically operates as a motherboard interconnect that links motherboard-mounted peripherals, such as graphics cards or wireless network cards. Although it is more of an interconnect interface than a storage interface, PCIe's excellent features for scalability, latency and performance make it a compelling interface choice for storage applications and solid state storage.
What are the benefits of the NVMe specification?
NVMe delivers faster access and consumes less power, thus reducing total cost of ownership (TCO) for enterprises and extending battery life for mobile clients. Compared with other interfaces designed for mechanical storage devices, NVMe reduces latency, and delivers higher Input/Output per Second (IOPS). NVMe also offers performance across multiple cores for quick access to critical data, scalability for current and future performance, and support for standard security protocols.
How does NVMe compare with other storage interfaces?
Seria ATA (SATA™), with its 3rd generation 6 Gb/s bandwidth, is currently the most widely used interface for hard disk drives (HDDs). Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI), the technical standard that specifies the operation of SATA host bus adapters, was designed to connect the CPU/memory subsystem with much slower rotating media-based storage. This renders the AHCI inefficient for the much faster SSDs, which behave more like DRAM than spinning media.
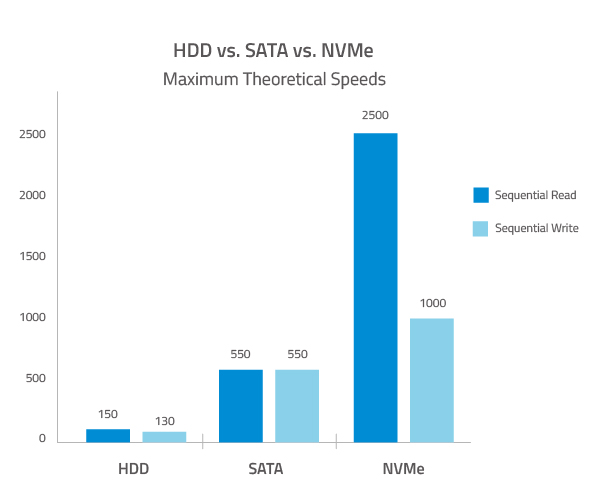
In random workloads, NVMe delivers 2X the performance of SAS 12 Gb/s, and 4-6X of SATA 6 Gb/s.
For sequential workloads, NVMe delivers 2X the performance of SAS 12 Gb/s, and 4X of SATA 6 Gb/s.
Source: “All About M.2 SSDs,” Storage Networking Industry Association (SNIA). 2014.
What are the differences between AHCI and NVMe?
AHCI, although compatible with SSDs, was designed for hard drives. AHCI was developed to connect the CPU/Memory subsystem with rotating storage media subsystem. The table below summarizes the differences between NVMe and AHCI device interfaces.
|
|
AHCI |
NVMe |
|
Maximum Queue Depth |
1 command queue 32 commands per queue |
64K queues 64K commands per queue |
|
Un-cacheable Register Accesses |
6 per non-queued command 9 per queued command |
2 per command |
|
MXI-X and Interrupt Steering |
Single interrupt, no steering |
2K MSI-X interrupts |
|
Parallelism and Multiple Threads |
Requires synchronization lock to issue command |
No locking |
|
Efficiency for 4KB Commands |
Command parameters require two serialized host DRAM fetches |
Command parameters in one 64B fetch |
Table 1. Technical differences between AHCI and NVMe. (Source: SATA-IO)
In what operating environments is NVMe supported?
NVMe is supported in the following environments:
|
|
Driver Available |
|
Chrome OS |
Chrome OS |
|
Windows |
Windows 7: 32-bit / 64-bit Service Pack 1 (SP1) + hotfix To download the hotfix, please visit https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/2990941/update-to-add-native-driver-support-in-nvm-express-in-windows-7-and-windows-server-2008-r2. Windows 8.1: 32-bit / 64-bit Windows 10: 32-bit / 64-bit Windows Server 2012 R2 |
|
Linux |
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 6.5, 6.6, 6.7, 7.0, 7.1 Ubuntu 16.04 |
What businesses will benefit most from NVMe?
NVMe was designed for both enterprise and client applications needing acceleration in critical data. Data centers will benefit greatly, as NVMe eliminates bottlenecks and provides capabilities to meet very demanding and time-sensitive requirements of cloud, Internet portal data centers, and other high-performance computing environments. Aside from enterprises and data centers, NVMe offers vast potentials in gaming, entertainment, and next-generation automobile applications.
What NVMe solutions are available from ATP Electronics?
ATP M.2 2280 NVMe SSDs are designed for a PCIe 3.0 x4 interface and comply with NVMe 1.2 specifications. Along with up to 1 TB memory capacity, sequential read speed of up to 2,540 MB/s, and sequential write speeds up to 1,100 MB/s, ATP M.2 NVMe SSDs exceed the SATA interface bandwidth 2x-3x, eliminate bottlenecks, and deliver a dramatic performance boost over AHCI standards. ATP M.2 2280 NVMe SSDs integrate 3D NAND MLC technology, enabling higher memory capacity, lower cost per bit, and increased longevity.
For more information on ATP's NVMe solutions, visit the ATP website or visit an ATP Distributor/Representative in your area.