What is M.2?
M.2 (pronounced “M dot two”) is a compact card or module form factor supporting multiple protocols and applications. It was developed by PCI-SIG and SATA-IO. The M.2 comes in two main formats:
- Connectorized
- Soldered down
Is M.2 the same as the NGFF?
M.2 was originally called the Next Generation Form Factor (NGFF).
It was formally renamed to M.2 in 2013.
What applications are M.2 modules targeted for?
M.2 is commonly used as solid state drives (SSDs) but can also be used for the following applications:
- Wi-Fi
- Bluetooth
- Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS)
- Near Field Communication (NFC)
- WiGig
- WWAN (2G, 3G, and 4G)
- Other and Future Solutions (e.g., Hybrid Digital Radio (HDR)
- Hardware Accelerator
What host interfaces are available for different M.2 modules?
The M.2 specification covers multiple Host Interface solutions including:
- PCI Express (PCIe)
- Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- High-Speed Inter-Chip (HSIC)
- SuperSpeed Inter-Chip (SSIC)
- Mobile PCIe (M-PCIe)
- Universal Serial Bus (USB)
- Secure Digital Input Output (SDIO)
- Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- Pulse Code Modulation / Inter-IC Sound (PCM/I2S)
- Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- System Management Bus (SMBus)
- Serial ATA (SATA)
- DisplayPort (DP)
- All future variants of the interfaces in this list
To ensure proper installation of M.2 modules, the M.2 standard in PCI Express M.2 Specification Revision 4.0 Version 1.0 has clearly distinguished “sockets” on the host. Each socket has a unique mechanical key, and modules are not interchangeable between sockets.
- Socket 1: Connectivity socket for Wi-Fi®, Bluetooth®, NFC (near-field communication) or Wi-Gig.
- Socket 2: WWAN/SSD/Other Socket that will support various WWAN+GNSS (global navigation satellite system) solutions, various SSD and SSD Cache configurations, and other yet-undefined solutions. (If the motherboard has a Socket 2 for a WWAN card and it is not in use, the socket may accommodate a B+M-keyed small M.2 SSD. Please refer to your motherboard documentation for details).
- Socket 3: SSD Drive Socket with SATA or up to four PCIe lanes.
|
Caution!
|
There are so many different sizes! How can I differentiate them to know which size fits on the motherboard, and what does the name on my M.2 card mean?
The card name provides several information about your M.2 card. For example, connectorized SSDs typically come in three dimensions: 2242, 2260, and 2280. The first two digits represent the width in millimeters (mm), while the last two digits represent the length in mm.
To standardize the names of different modules, a naming convention is defined in PCI Express M.2 Specification Revision 4.0 Version 1.0. The following table defines the size, component assembly (single-/double-sided, maximum height), interface, and other important information about the card.
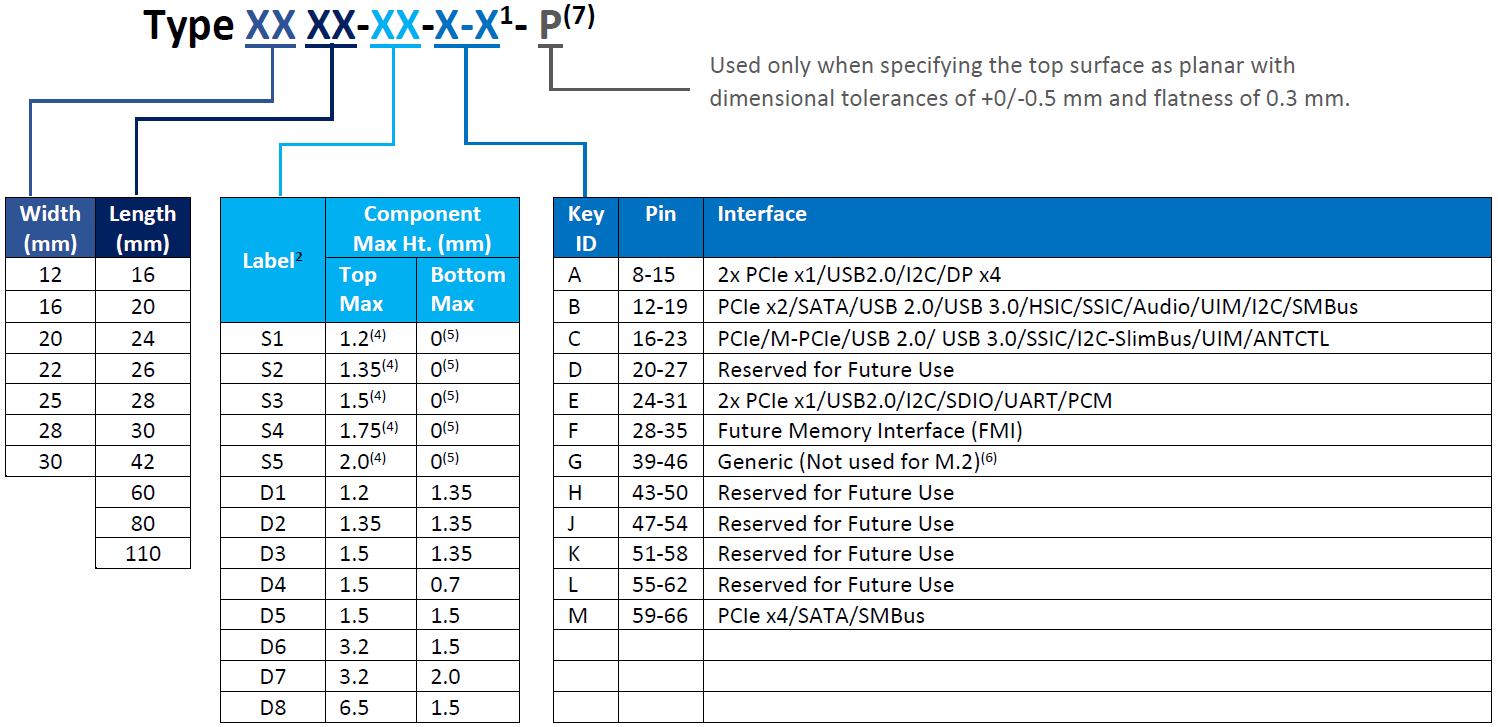
M.2 Card Type Naming Convention (Source: PCI Express M.2 Specification Revision 4.0 Version 1.0)
NOTES:
- Use ONLY when a double slot is being specified.
- Label included in height dimension.
- This dimension is 11.5 mm but is written as 11 in Type name (i.e., BGA Type 1113).
- For BGA SSD, maximum height is measured with the solder balls collapsed and is valid whether the BGA is located directly on a platform or mounted on a module board.
- Insulating label allowed on connector-based design.
- Key G is intended for customer use. Devices with this key will not be M.2-compliant. To be used at customer’s risk.
- Use only when specifying the top surface as planar.
From the naming convention table above, we can deduce the following information from these examples:

ATP NVMe M.2 2280 D2-M
This module is 22 mm wide and 80 mm long; it is double-sided, with components installed on
both top and bottom not exceeding 1.35 mm in height; and, it is “M” keyed.

ATP SATA M.2 2242-D2-B-M
This module is 22 mm wide and 42 mm long; it is double-sided, with components installed on both top and bottom not exceeding 1.35 mm in height; and, it is “B+M” keyed.
Why do the edge connectors on M.2 modules look different? How do I know which M.2 card I need?
The edge connectors are also called “keys.” They are used to prevent insertion to an incompatible socket on the host.
The M.2 specification identifies 12 key IDs on the module card and socket interface, but M.2 SSDs typically use three common keys: B, M, and B+M. You will find the key type labeled on or near the edge connector (or gold fingers) of the SSD.
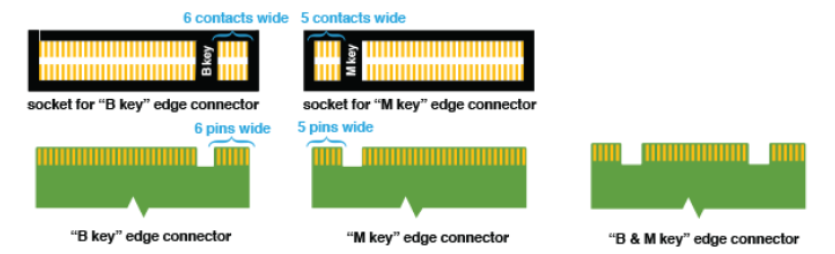
M.2 Edge Connector Keys (Source: How to Geek.com)
ATP M.2 SSDs and their edge connectors
What protocols and interfaces do M.2 SSDs support?
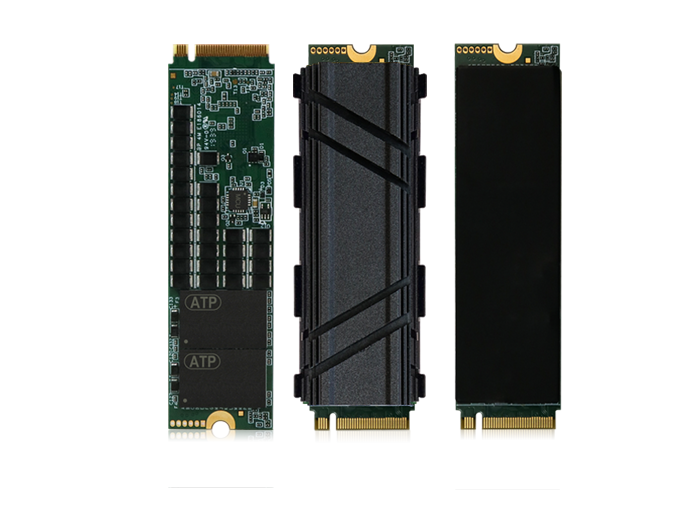
M.2 SSDs support both NVMe protocol using PCIe interface and AHCI using SATA interface.ATP offers connectorized modules supporting NVMe and SATA as well as soldered-down NVMe heatsink BGA (HSBGA) SSDs.
For an in-depth discussion on how NVMe M.2 SSDs differ from SATA M.2 SSDs, please have a look at a previous blog entry here.
What are the benefits of a soldered-down M.2 solution?
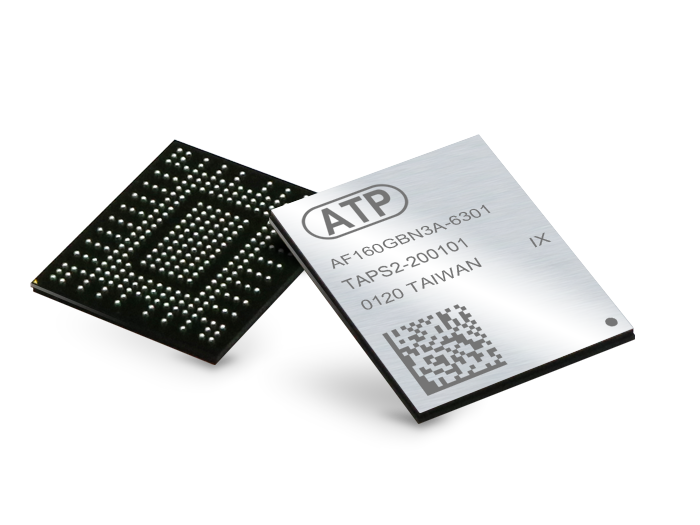
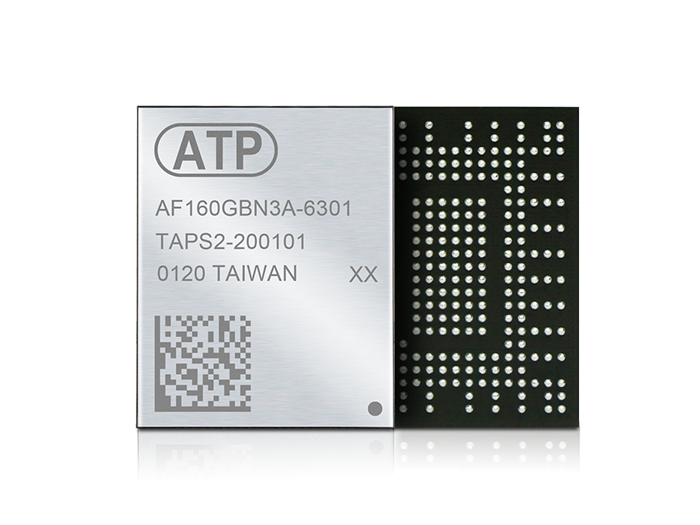
Soldered-down solutions such as ATP’s M.2 Type 1620 heatsink ball-grid array (HSBGA) offers NVMe performance in a shock/vibration resistant package, while the 291-ball packaging takes up minimal space within tightly confined systems. The optimized power consumption of just 5 mW during Power State 4 (Sleep Mode) also translates to big power savings.
Supporting high-speed PCIe 3.0 interface x4 lanes and NVMe protocol, this tiny SSD delivers up to 32 Gb/s bandwidth at 8 Gb/s per lane. BGA SSD technology allows the NAND flash and controller to be integrated into one package that is lightweight yet offers powerhouse performance, ample capacities, and other advanced features to meet the portability and reliability requirements of ultra-compact Internet of Things (IoT) devices and embedded systems.
Due to their compact form factor, NVMe M.2 SSDs are typically installed in tight spaces with limited or no airflow. And since they run at blazing-fast speeds, overheating could be a major concern. How can overheating be prevented when using M.2 SSDs?
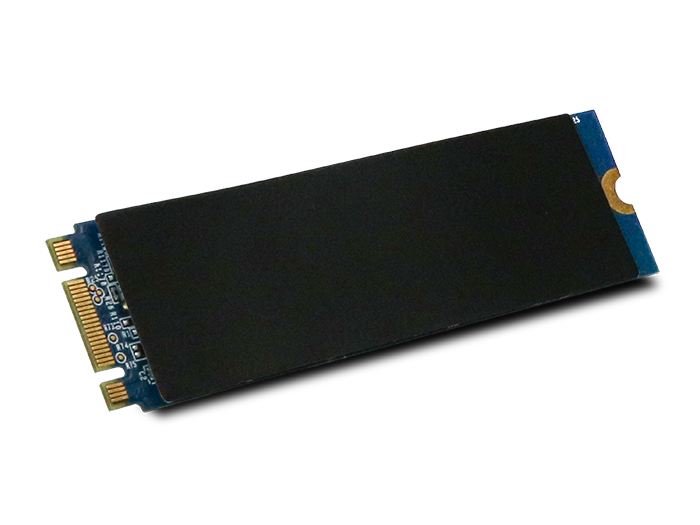
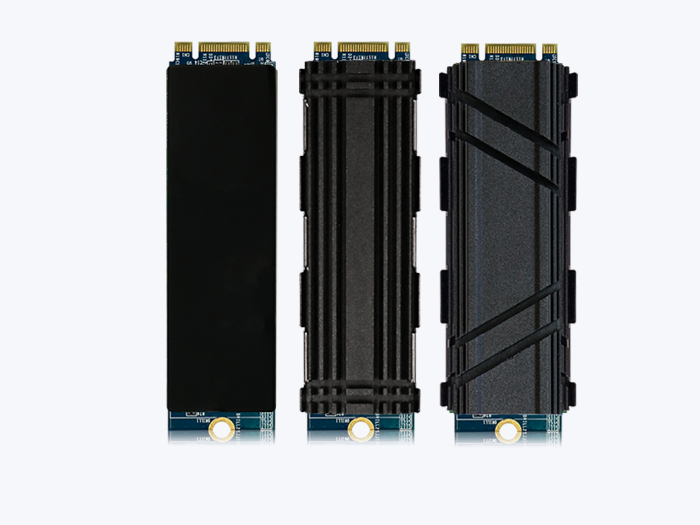
For soldered-down solutions like the NVMe M.2 HSBGA, these SSDs are outfitted with a heatsink on top, which complements system airflow to enhance heat dissipation and keep the BGA SSD cool while offering 2X-3X better sustainable performance.
For connectorized solutions like the NVMe M.2 2280, ATP offers customizable Thermal Management Solution, which includes copper foil and fin-type heatsink options. They are recommended for applications requiring stable and sustained read/write performance at high temperatures.
For more information on how ATP mitigates overheating through customizable solutions, please visit this page.
Different applications require different solutions. My organization wants to custom-configure M.2 SSDs to fit specialized requirements in thermal, endurance and other configurations. Can ATP meet our special needs?
Customization is one of our key specializations. As a true manufacturer for 30 years, we have control over all aspects of the design, production, and supply of our products; hence, we are totally capable of meeting your organization’s specialized requirements. We can customize hardware, firmware and software to provide the most suitable solutions for your memory and storage needs.
For more information on ATP’s extensive range of products and services, please visit https://www.atpinc.com/ or contact an ATP Representative in your area.